Program Overview
How and where we live, eat, sleep, work, and play, can have huge impacts on our health! These factors have especially large impacts during pregnancy and in early child years, but continue to be vital throughout our lives. We created Prescriptions for Prevention to guide parents and caregivers in the best actions they can take to protect children’s environmental health and prevent future harm. These materials are based off of our clinician facing Pediatric Environmental Health Toolkit (PEHT), featuring evidence-based overviews on health hazards related to air, water, food and consumer products. Two key groups of concern are Hazards, and Sources. Hazards are the different kinds of harms we are concerned about, like groups of toxic chemicals. Sources are where harms may come from, like our food or water.
Program Materials
This document addresses arsenic exposure, its sources (such as contaminated water and certain foods), health effects, and preventive strategies to minimize risk. It emphasizes the importance of testing water sources and being aware of dietary intake.
This factsheet outlines the hazards of asbestos exposure, commonly found in older building materials. It details health risks like lung diseases and mesothelioma, identifies potential asbestos-containing materials, and advises on safe handling and abatement procedures.
This document examines the presence of heavy metals in baby food, their potential health impacts on infants, and recommendations for parents to reduce exposure. It suggests diversifying diets and choosing products tested for contaminants.
This factsheet focuses on Bisphenol A (BPA), a chemical used in plastics and resins. It discusses sources of BPA exposure, associated health concerns, and tips to limit contact, such as using BPA-free products and avoiding microwaving plastics.
Carbon Monoxide (CO) Environmental Exposure: This factsheet highlights the dangers of carbon monoxide—a colorless, odorless gas produced by burning fuels—and offers preventive measures such as installing CO detectors and ensuring proper ventilation to prevent poisoning.
This document provides an overview of health risks from chemical exposures in everyday environments, with a focus on prevention strategies and safer alternatives.
Consumer Products: This document discusses potential chemical hazards in everyday consumer products, advising the use of safer alternatives and providing resources to make informed choices to reduce exposure to harmful substances.
Dust: This factsheet addresses the health risks associated with household dust, which can contain harmful contaminants, and recommends cleaning practices to minimize exposure, especially for children.
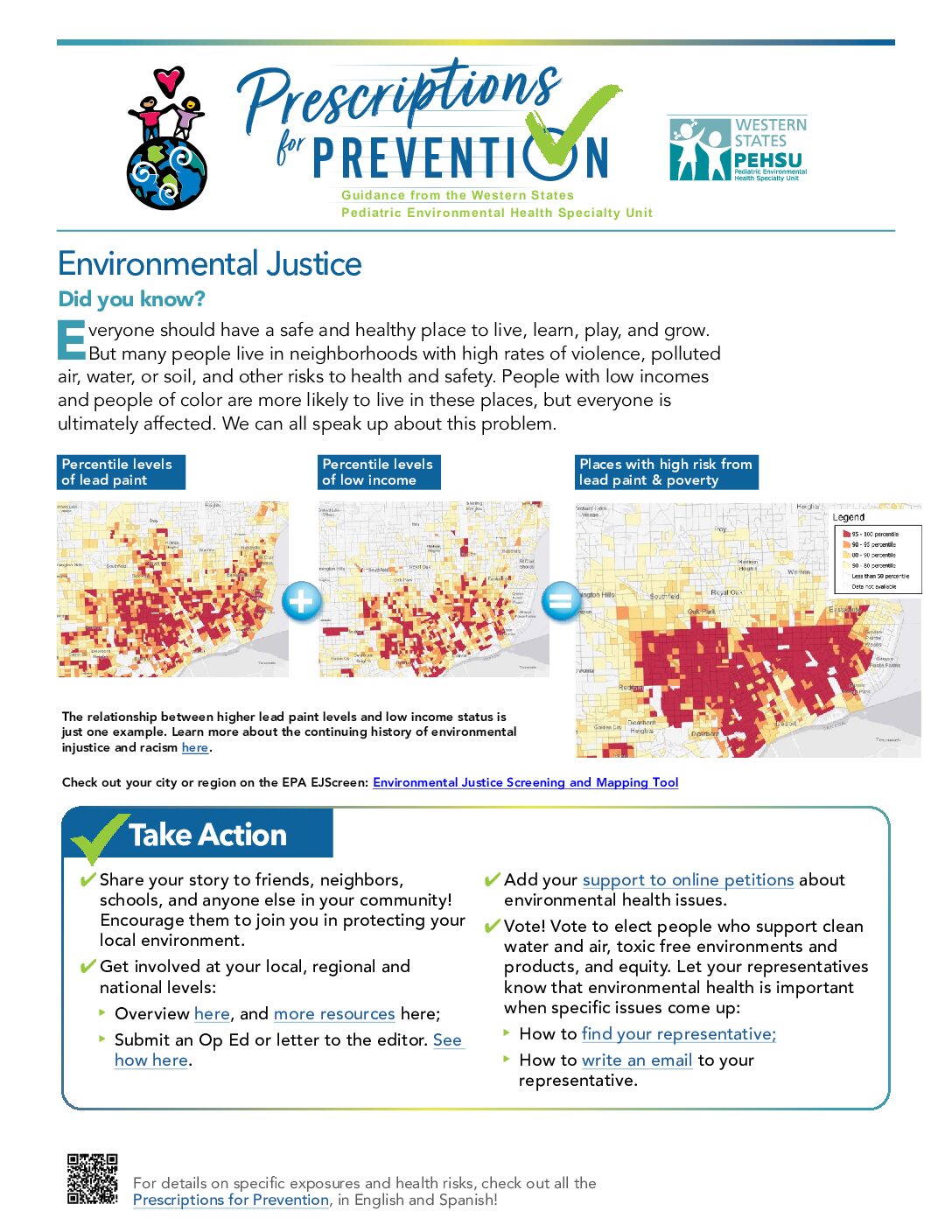
This factsheet discusses the disproportionate environmental health burdens faced by marginalized communities and advocates for equitable policies and protections.
This resource explains the main routes of environmental exposure—ingestion, inhalation, and dermal contact—and provides strategies to minimize risks across different settings.
This document highlights the health impacts of extreme weather, such as heat stress and air pollution, and emphasizes the need for mitigation and adaptation strategies to protect vulnerable populations.
This PDF provides a fact sheet highlighting the impacts of extreme weather on children’s health and offers actionable prevention strategies for healthcare providers, educators, and communities.
This factsheet examines the use of PBDEs as flame retardants, their potential health impacts, and tips to reduce exposure in homes and workplaces.
Nitrates in Food and Water: This document explains how nitrates from fertilizers and preservatives can contaminate food and water, posing health risks like “blue baby syndrome,” and suggests testing water sources and dietary precautions to reduce exposure.
This factsheet explores the benefits and potential contaminants in milk, offering recommendations for safer consumption to protect both infant and maternal health.
Particles and Nitrogen Oxides Environmental Exposure: This factsheet discusses the health impacts of particulate matter and nitrogen oxides from combustion processes, offering strategies to monitor air quality and reduce personal exposure.
This document provides comprehensive information on the sources of lead exposure, its health effects, and strategies for prevention, emphasizing the importance of public health measures to reduce lead-related risks.
Baby Food: This factsheet highlights concerns about heavy metals in baby foods and recommends feeding children a variety of fruits and vegetables, choosing products tested for contaminants, and preparing fresh foods when possible to minimize exposure.
This document discusses the health impacts of mold exposure in homes and provides tips for identifying, removing, and preventing mold growth.
This factsheet highlights environmental health risks during natural disasters and offers preparedness strategies to minimize exposure to harmful contaminants.
This document outlines the risks of nitrate contamination in food and water, especially for infants, and provides steps for testing and reducing exposure.
This factsheet focuses on pollutants affecting outdoor air quality, their health impacts, and actions individuals and communities can take to reduce exposure.
This document details the sources and health effects of PAHs, chemicals released during combustion, and suggests measures to limit contact.
This factsheet discusses the dangers of particulate matter in air pollution, its effects on respiratory and cardiovascular health, and ways to mitigate exposure.
This factsheet discusses the health risks of pesticide exposure, particularly for children, and offers tips for reducing exposure in homes, gardens, and food.
This document highlights the widespread use of PFAS chemicals, their persistence in the environment, and health concerns, with advice on minimizing exposure.
This factsheet outlines the sources and health risks of phthalates, commonly found in plastics and personal care products, and provides recommendations for avoidance.
This document examines the environmental and health impacts of plastic use, focusing on microplastics and chemical leaching, with strategies to reduce exposure.
This document covers the history, health risks, and current issues related to PCBs, advising on strategies to avoid exposure.
This factsheet discusses radon, a radioactive gas linked to lung cancer, and provides guidance on testing and mitigating radon levels in homes.
This factsheet discusses the health risks associated with secondhand smoke exposure. It highlights the dangers to both children and adults, provides statistics on exposure rates, and suggests measures to reduce involuntary inhalation of tobacco smoke.
This document addresses health risks from contaminated soil, especially for children and gardeners, and offers tips for safe gardening practices.
This resource explores how urban planning and the built environment impact health, emphasizing the importance of access to green spaces, clean air, and safe infrastructure.
This document explores why children are more susceptible to environmental hazards due to their developing systems and behaviors, offering guidelines for enhanced protection.
This factsheet focuses on the specific risks of environmental exposures during pregnancy and their potential impacts on fetal development, stressing the importance of preventive measures.
This factsheet highlights the sources of VOCs, their health effects, and strategies to improve indoor air quality by reducing VOC exposure.
This document covers common water contaminants, their health risks, and steps to ensure safe drinking water through testing and filtration.
Program Videos
A’afiaga o le soifua maloloina i mea’ai e i ai u’amea mamafa
O lenei vitio o loʻo faʻamatalaina ai le soifua maloloina o uʻamea mamafa i meaʻai ma tuʻuina atu fautuaga e faʻaitiitia ai le aafia i vailaʻau oona.
Children’s Health and the Impacts of Plastics
This video discusses how plastic can release harmful particles into our food, water, and environment, posing significant health risks—especially for children—and explores alternatives.
Extreme Weather, Heat Stress and Health
This video explores how extreme weather increases the risk of heat illness, especially for children and pregnant individuals, and discusses community action essential for protection.
Health effects of heavy metals in food
This video outlines the health effects of heavy metals in food and provides tips to minimize exposure to toxic chemicals.
Keep Kids Healthy by Preparing for Natural Disasters
This video provides advice on preparing for natural disasters, emphasizing safety precautions for children and pregnant individuals.
Mga epekto sa kalusugan ng mataas na antas ng metal sa pagkain
Binabalangkas ng video na ito ang mga epekto sa kalusugan ng mabibigat na metal sa pagkain at nagbibigay ng mga tip upang mabawasan ang pagkakalantad sa mga nakakalason na kemikal.
Developed in partnership with:

This project was led by: James Earl Schier Nolan, MPH (WS PEHSU and EaRTH Center), Stephanie Holm, MD, PhD, MPH, Mark Miller, MD, MPH and Maria Valenti. Graphic design by Steve Burdick.
Contributors and subject authors include: Content contributors include: Anthony Lopez, Bryan Ramirez, Elizabeth Cheung, Erica Chung, Hannah El-Sabrout, Ignacio “Nacho” Santana, Jose Maldonado, Kali Sullivan, Keo Chui, Madeleine Ambrose, Natasha Gonzalez, Nathaniel Tsiperfal, Rachana Mudipalli, Sonja Swenson, Valerie Gallardo, and Zoë Gilbard.
Project supported by: the UCSF Environmental Research and Translation for Health (EaRTH) Center via the core center grant P30-ES030284 from the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, and the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), funded (in part) by a cooperative agreement with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (CDC/ATSDR). The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) supports the PEHSUs by providing partial funding to CDC/ATSDR through an Inter-Agency Agreement. The findings and conclusions presented have not been formally disseminated by CDC/ATSDR, NIEHS, or EPA and should not be construed to represent any agency determination or policy. Use of trade names that may be mentioned is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by the CDC/ATSDR, NIEHS, or EPA.